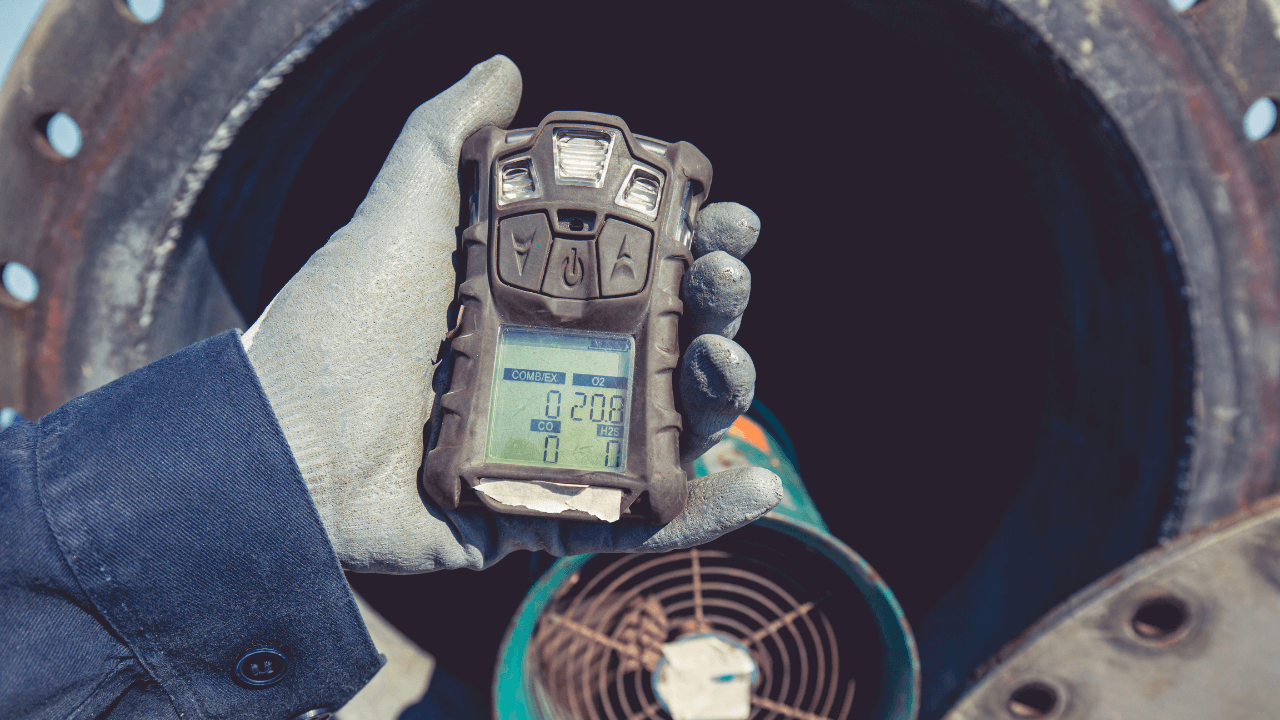
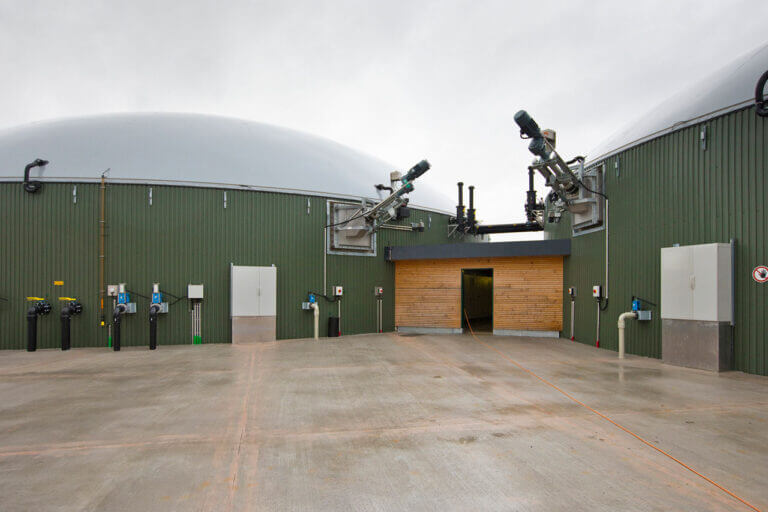
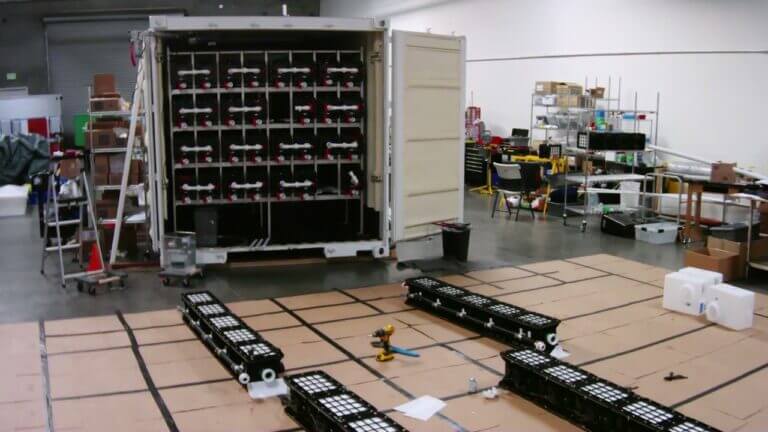
When it comes to managing wastewater, removing hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is non-negotiable. This gas, notorious for its toxic, corrosive nature and pungent odor, poses severe risks to health, safety, and operational efficiency for industrial and municipal facilities.
While numerous methods exist for H2S removal, the question remains: Are these methods the most effective and sustainable in today’s demanding environment? Or are you just settling?
Existing H2S Removal Techniques
Historically, facilities have relied on methods such as chemical treatments, biofilters, and air scrubbers to combat H2S.
Chemical treatments often involve the use of oxidizing agents like chlorine, ozone, or hydrogen peroxide to convert H2S into less harmful compounds. While these methods are effective in reducing H2S, they require continuous chemical input and monitoring, leading to increased operational costs .
Biofilters utilize microorganisms to oxidize H2S into less harmful compounds. Their performance, however, is highly dependent on environmental conditions like temperature and humidity, and they struggle to manage sudden spikes in H2S levels, leading to potential gas leaks, risking safety and compliance. Most biofilters also require the addition of nutrients to ensure a healthy biomass with higher H2S removal efficiencies.
There are wet and dry air scrubbers available to adsorb gaseous H2S into a scrubbing liquid or dry media. These methods are proven but both require extracting H2S gas from headspaces into a chamber that is either sprayed with a scrubbing liquid or packed with solid absorption media. In the case of liquid scrubbers, the H2S-containing liquid must be appropriately captured and managed. The media in dry scrubbers will require periodic disposal and replacement. While these methods reduce H2S levels, they can require significant energy and maintenance, often leading to high operational costs and inefficiencies, particularly during high-production periods.
While these techniques are the standard for removing H2S from wastewater, they have their drawbacks. With the exception of in-tank oxidation techniques with added chemicals, there are no existing methods that capture H2S before it is released into the tank headspace.
The Limitations of Traditional H2S Removal Systems
- Inefficiency
Traditional H2S removal systems often struggle to maintain consistent and safe levels of H2S, particularly during periods of high or variable H2S production. The fluctuating nature of industrial wastewater composition means that these systems can easily become overwhelmed, leading to H2S levels that exceed safety and regulatory limits. This inconsistency poses significant risks to both worker safety and regulatory compliance.
- High Maintenance
One of the most significant drawbacks of traditional H2S removal systems is the high maintenance they require. Frequent maintenance is not just a minor inconvenience; it leads to increased downtime, higher labor costs, and ultimately, reduced operational efficiency. Systems that require constant attention drain resources and can lead to extended periods of reduced productivity, which is costly for any facility.
- Biofilter Sludge Buildup
Sludge accumulation is another critical issue with traditional biological H2S removal methods. Over time, sludge can build up in treatment systems, reducing their efficiency and creating additional waste management challenges. This sludge not only clogs up the system but also requires frequent removal and disposal, adding to the operational burden.
- Energy and Chemical Costs
Traditional systems are notorious for their high energy consumption and reliance on chemicals, both of which drive up operational costs. The constant need for chemical inputs and the energy required to run these systems make them less sustainable and more expensive over time. In an era where sustainability is not just a goal but a necessity, these systems fall short.
The Risks of Complacency
Serious compliance risks, including hefty fines, legal actions, and potential shutdowns can occur without reliable H2S removal solutions. As regulations increase, conventional methods may no longer meet standards, putting facilities at risk of falling out of compliance. The resulting financial penalties and damage to a company’s reputation can be significant.
Traditional H2S systems also pose sustainability risks, with high energy use and chemical reliance and the environmental impact and ongoing costs of managing sludge and secondary byproducts.
But, most important of all, ineffective H2S management can compromise worker safety, leading to dangerous exposure levels and severe health risks. Minor exposure to H2S gas can cause coughing and irritation, while higher exposure is much more severe and even deadly.
Sticking with the status quo is no longer an option.
Don’t Risk Your Safety
We cannot overstate the importance of effective H2S removal. Industrial and municipal facilities that fail to manage H2S levels not only put their operations at risk but also endanger the health and safety of their workers.
But there’s good news on the horizon.
We have designed a system that addresses the shortfalls of traditional H2S removal technologies and can complement existing equipment. By offering a safer, more efficient, and cost-effective solution, this innovative system is set to redefine H2S management in storage tanks, ensuring that your facility remains compliant, operational, and, most importantly, safe.
Stay tuned as we unveil a solution that truly delivers where others fall short.
📩Sign up here to be the first to know about the technology that is changing the landscape of H2S management: